What causes Warts on Fingers – The wart is a proliferation of skin caused by some strains of the virus called human papillomavirus (HPV).
The HPV virus infects the upper layer of skin, usually entering the body through a cutaneous lesion.
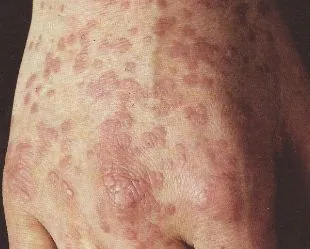
The virus causes rapid growth of the upper layer of the skin, forming a wart.
Warts can grow anywhere in the body and are most common among:
- Children,
- Young.
Types of Warts
The common wart (also known as vulgar) develops often on the hands but can occur anywhere on the body.
These skin formations are solid, flattened and grayish-brownish-yellow in color.
Only hurt when you put pressure on them.
They cannot be mistaken for a spine that is red in color.
The plantar wart grows on the soles of the feet, often at the base of the big toe, but can also grow:
- Under the heel,
- At your fingertips.
Plantar warts can be distinguished from:
- Simple plantar wart: It looks like a hard, thick skin plaque with some dark spots in the center.
Plantar warts can cause foot pain when walking; the person may have the sensation of walking on gravel. - The mosaic plantar wart is a subtype characterized by many small intertwined warts that have the shape of a mosaic.
They are less common and more superficial than the simple plantar wart.
The nail and periungual warts
Appear below and around the nails of the hands and feet.
They look rough with uneven surface and edges. They can affect nail growth.
The flat wart is a smooth swelling that usually grows in groups on the face, arms or legs.
They are:
- Common in children,
- Less frequent in adolescence,
- Rare in adults.
It is small (between 2 and 4 mm in diameter, usually less than the edge of a pencil eraser), flat and may have color:
- Pink,
- Reddish,
- Brown,
- Light yellow.
The filiform wart usually grows around the area of the mouth, nose or beard. It is the same skin color and has lumps that look like wires coming out of the wart.
Warts or papillomas
- Anogenital warts: They are usually asymptomatic but can cause discomfort and itching. Genital warts can be located on both the skin and mucous membranes.
- Warts on the larynx (pachydermia) is a benign mass that can cause disturbances in phonation (when spoken) and often must be removed.
What is a periungual wart and what does it look like?
Periungual warts are abnormal formations that are difficult to notice in the initial phase.
In the beginning, they are the size of a pinhead and are smooth, so people do not notice their presence until they grow sufficiently.
Over the weeks periungual warts grow and develop irregular and rough edges that can affect the growth of the nail.
The consequence may be the fall.
In extreme cases, the nails can become deformed and damaged forever. If the wart is not treated and worsens, it may move to the base of the nail bed, causing a serious infection.
Genital warts
Genital warts (sometimes called condyloma acuminata or venereal warts) are the typical sign of genital infection by the human papillomavirus. Many people, however, have an infection genital HPV without genital warts.
Genital warts are:
- Soft,
- Wet,
- The color of the skin.
They appear within a few weeks or months after infection.
Usually located:
- In the genitals,
- In the pubic region.
Sometimes they occur in clusters and resemble the shape of cauliflower, can be raised or flat, small to very large.
- In women, genital warts may be present in the vulva and cervix or in and around the v*gina and anus.
- In men, genital warts can appear on the p*nis, glans, or scrotum.
There are cases where genital warts are located in the thigh and groin.
These lumps should not be confused with genital herpes vesicles.
Transmission of genital warts
Genital warts are very contagious.
It is possible to get them during unprotected, oral, v*ginal or anal intercourse with an infected partner.
Contamination can also occur through skin-to-skin contact, for example during v*ginal, anal or oral s*x (rarely) with someone who is infected.
About two-thirds of people who have s*xual contact with a partner who has genital warts develop warts, usually within 3 months after contact.
Complications of genital warts
Cancer
Some types of HPV (mainly 16 and 18) can cause cancer:
- In the cervix.
- Vulvar,
- In the p*nis (rare),
- Anal.
Most genital HPV infections do not become cancer.
In women, a Pap test detects any abnormal cells in the cervix.
In men, HPV complications are diagnosed by:
- Colonoscopy,
- Anoscopy.
Pregnancy and childbirth
Genital warts can cause a lot of problems during pregnancy.
Since genital warts can multiply and increase, the doctor explains the options for removal if necessary.
Genital warts can also be removed to ensure safe and healthy delivery of the newborn.
Sometimes it gets bigger during pregnancy and if the warts are located in the urinary tract can cause difficulties to urinate.
If the warts are in the v*gina:
- They can make the v*gina less elastic,
- Causes obstruction during labor.
Warts are contagious
Contagion is not guaranteed simply by touching someones wart.
The viruses that cause warts pass from one person to another through physical contact or by touching a surface that was in contact with a person who had a wart, such as:
- A bathroom rug,
- The shower floor.
A small cut or injury to the skin can make any area of the skin more vulnerable to warts.
In addition, a wart can contaminate other parts of the body.
The time interval between when someone is exposed to the virus and the wart formation is variable.
Warts can grow very slowly and can take several weeks to develop.
Symptoms of warts
- Most warts are raised with a rough surface.
- They can be round or oval.
- The place where the warts are may be lighter or darker in relation to the tone of the skin.
- Rarely, the warts are black.
- Some warts have smooth or flat surfaces.
- The wart can become swollen and inflamed, and can also cause pain and itching.
Tests and diagnosis of plantar wart
The doctor can diagnose a wart by looking only at the ball on the skin.
Sometimes the doctor can scrape the top layer of the wart to look for clotted blood vessels (black spots) that often occur in the case of warts.
If there is still doubt in the diagnosis, the doctor can collect a small sample of skin for analysis in the laboratory, to discard other types of skin formations.
For the differential diagnosis of the wart should be excluded:
- Calo (tiloma)
- Nevo
- Important keratolysis
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Seborrheic or actinic keratosis
- Keratoacanthoma
Difference between wart and callus or callosity
The plantar wart causes pain when walking. The weight of the body causes a boost in depth.
The wart has black spots that are characteristic and represent coagulated blood vessels.
It bleeds when the person tries to scratch.
Avoid cutting the wart because:
- You can appeal,
- It can expand,
- Other warts may form nearby.
The callus develops behind the heel and at the base of the toes, while the wart occurs in the parts where there is no friction and in the softest parts.
Home Remedies for Wart
If the person treats the wart at home, he should:
- Dip the wart in warm water and remove dead skin from the surface of the wart with a nail file (which can no longer be used for nails) before applying for the medicine.
- Be careful not to scratch the healthy skin around the wart.
- Keep the wart area covered while the medicine works.
- Do not rub, scratch or pierce the wart to prevent the spread of the virus to another part of the body.
Ask your doctor if this type of home treatment is appropriate.
